介绍使用 rustup 管理 Rust 工具链,Rust 程序的目录布局,编译链接和 Cargo 配置。
rustup 和 toolchain #
rustup 用于管理 rust toolchain 和一些额外工具(称为 component,如 rust-analyzer,通过预定义的 profile 来定义 components 集合)。
rustup show: 显示按照和缺省的 toolchainsrustup update: 更新所有的 toolchainsrustup defaultTOOLCHAIN: 设置缺省的 toolchainrustup component list: 列出可用的 componentsrustup component add NAME: 添加 componentrustup target list: 列出可用的编译器 targetrustup target add NAME: 添加一个编译器 target
# curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
brew install rustup
rustup default stable
rustup component add clippy # rust lints
rustup component add rustfmt # rust formater
rustup component add rust-src # rust 源文件
rustup component add rust-docs # 添加 rust 标准库文档
# 查看已安装的工具链
rustup toolchain list
# 安装 nightly 工具链
rustup toolchain install nightly
# 设置缺省工具链为 nightly
rustup default nightly
# cargo 支持在命令行上使用 +toolchain 指定工具链版本(rustup toolchain list 或 rustup show 查看列表)
cargo +nightly expand
rustup 可以安装多套 toolchain 和 target,使用 rustup show 命令来查看:
$ rustup show
Default host: x86_64-apple-darwin # 当前 host architecture:
rustup home: /Users/zhangjun/.rustup
installed toolchains
--------------------
nightly-2023-11-14-x86_64-apple-darwin
nightly-x86_64-apple-darwin (default)
esp
installed targets for active toolchain
--------------------------------------
riscv32imac-unknown-none-elf
riscv32imafc-unknown-none-elf
riscv32imc-unknown-none-elf
x86_64-apple-darwin
active toolchain
----------------
nightly-x86_64-apple-darwin (default)
rustc 1.78.0-nightly (fc3800f65 2024-02-26)
使用 rustup default nightly 指定 缺省 toolchain ,这时 cargo/rustc 等指向该 toolchain 下的 binary:
$ cat ~/.rustup/settings.toml
default_toolchain = "nightly-x86_64-apple-darwin"
profile = "default"
version = "12"
$ ls ~/.rustup/toolchains/
esp/ nightly-2023-11-14-x86_64-apple-darwin/ nightly-x86_64-apple-darwin/
$ ls -l ~/.rustup/toolchains/nightly-x86_64-apple-darwin/bin/
total 100M
-rwxr-xr-x 1 zhangjun 30M 2 27 11:51 cargo*
-rwxr-xr-x 1 zhangjun 1.1M 2 27 11:51 cargo-clippy*
-rwxr-xr-x 1 zhangjun 1.6M 2 27 11:52 cargo-fmt*
-rwxr-xr-x 1 zhangjun 11M 2 27 11:51 clippy-driver*
-rwxr-xr-x 1 zhangjun 38M 2 27 11:51 rust-analyzer*
-rwxr-xr-x 1 zhangjun 980 2 27 11:51 rust-gdb*
-rwxr-xr-x 1 zhangjun 2.2K 2 27 11:52 rust-gdbgui*
-rwxr-xr-x 1 zhangjun 1.1K 2 27 11:51 rust-lldb*
-rwxr-xr-x 1 zhangjun 598K 2 27 11:52 rustc*
-rwxr-xr-x 1 zhangjun 12M 2 27 11:52 rustdoc*
-rwxr-xr-x 1 zhangjun 6.9M 2 27 11:52 rustfmt*
还可以通过 cargo 命令行参数或 rust-toolchain.toml 文件来 by 项目指定 toolchain 。
cargo 命令行参数:+toolchain 指定 toolchain,如:
cargo +nightly build --out-dir=out -Z unstable-options # 使用 nightly toolchain
cargo +esp fetch # 使用 esp toolchain
在项目根目录下创建 rust-toolchain.toml 文件,也可以 by 项目指定 rust toolchain 版本、component 和 targets ,后续执行 cargo build 时会自动安装和使用它们:
[toolchain]
# 指定使用的 toolchain channel
channel = "1.85" # "nightly-2020-07-10"
# profile 用于定义要下载的 component 集合,默认有三种:minimal,default,complete
profile = "minimal"
# 需要额外安装的 components
components = [ "rustfmt", "clippy" ]
# 除了 host target 外需要额外安装的 target,如交叉编译的 target。
targets = [ "x86_64-apple-darwin", "aarch64-apple-darwin", "x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu", "wasm32-wasip1", "x86_64-pc-windows-msvc" ]
rustup 安装的 toolchain 的根目录称为 sysroot。
# 查看当前使用的 toolchain 的 sysroot 目录
$ rustc --print=sysroot
/Users/zhangjun/.rustup/toolchains/nightly-x86_64-apple-darwin
$ ls /Users/zhangjun/.rustup/toolchains/nightly-x86_64-apple-darwin
bin/ etc/ lib/ libexec/ share/
# lib/rustlib 目录包含 toolchain 支持的 target
❯ ls -l /Users/alizj/.rustup/toolchains/stable-aarch64-apple-darwin/lib/rustlib
total 1.4M
drwxr-xr-x 4 alizj 128 Nov 11 10:21 aarch64-apple-darwin/ # 该 toolchian host target
drwxr-xr-x 3 alizj 96 Nov 11 10:20 aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu/ # 该 toolchain 支持的其它 target
drwxr-xr-x 3 alizj 96 Nov 11 10:20 aarch64-unknown-linux-musl/
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 412 Nov 11 10:21 components
#...
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 1 Nov 11 10:21 rust-installer-version
drwxr-xr-x 3 alizj 96 Nov 11 10:20 src/
drwxr-xr-x 3 alizj 96 Nov 11 10:20 wasm32-unknown-unknown/
drwxr-xr-x 3 alizj 96 Nov 11 10:20 x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/
drwxr-xr-x 3 alizj 96 Nov 11 10:20 x86_64-unknown-linux-musl/
# lib/rustlib/<target>/lib/libstd.*.dylib 为该 target 的 Rust 标准库
❯ ls -l /Users/alizj/.rustup/toolchains/stable-aarch64-apple-darwin/lib/rustlib/aarch64-apple-darwin/lib/
total 127M
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 462K Nov 11 10:21 libaddr2line-520c17beaa93f971.rlib
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 27K Nov 11 10:21 libadler2-34600ea6a0627d34.rlib
#...
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 1.5M Nov 11 10:21 librustc-stable_rt.lsan.dylib
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 3.6M Nov 11 10:21 librustc-stable_rt.tsan.dylib
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 338K Nov 11 10:21 libstd_detect-a7040f5c30705370.rlib
-rwxr-xr-x 1 alizj 9.2M Nov 11 10:21 libstd-478fce78004a205f.dylib* # Rust 标准库
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 16M Nov 11 10:21 libstd-478fce78004a205f.rlib
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 6.0K Nov 11 10:21 libsysroot-fe11166008981ac0.rlib
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 6.0M Nov 11 10:21 libtest-e55f0e5fbeb5b470.rlib
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 25K Nov 11 10:21 libunwind-1eac9fcb2d5c62fe.rlib
对于嵌入式设备,如 esp32,官方不支持它的 target,故不提供预编译的 Rust 标准库二进制,需要每次都重新编译构建 std 库;
- 通过项目
.cargo/config.toml中的[unstable] build-std = ["std", "panic_abort"]来配置;
$ ~/.rustup/toolchains/esp/bin/rustc --print=sysroot
/Users/zhangjun/.rustup/toolchains/esp
$ ls /Users/zhangjun/.rustup/toolchains/esp
bin/ etc/ lib/ libexec/ share/ xtensa-esp-elf/ xtensa-esp32-elf-clang/
cargo 配置和命令 #
cargo 有两种配置文件:
- 用户缺省配置文件(可以通过 CARGO_HOME 环境配置,默认为
~/.cargo):~/.cargo/config.toml; - by workspace 或 package 配置文件:
.cargo/config.toml;
Cargo Home 默认为 ~/.cargo,或者由环境变量 CARGO_HOME 指定, 用于保存 Cargo 个人全局配置参数以及下载的 crate 包和依赖。
❯ ls -l ~/.cargo/
total 8.0K
drwxr-xr-x 29 zj 928 Jul 21 16:50 bin/ # cargo install 或 rustup 安装的 binary
-rw-r--r-- 1 zj 245 Dec 6 2024 config.toml # 个人全局缺省配置参数
-rw-r--r-- 1 zj 300 Mar 28 2024 env
drwxr-xr-x 5 zj 160 May 5 2024 git/
drwxr-xr-x 6 zj 192 Mar 28 2024 registry/ # 从 registry crates.io 下载的包,可以使用 cargo cache 命令自动清理
常用 cargo 命令:
cargo install: 从 crates.io 安装 binary package,默认安装到~/.cargo/bin目录;cargo new hello_world: 创建一个 binary package,入口为src/main.rs文件;cargo new hello_world --lib:创建一个 library package,入口为src/lib.rs文件;cargo add tokio --features macros,rt-multi-thread: 给项目添加依赖,同时指定开启的 features;cargo build:使用 debug 构建项目,保存到 target/debug 目录,产生 Cargo.lock 文件;cargo build --release:使用 release 构建项目,开启 optimization,保存到 target/release 目录;cargo clean && cargo build --release --quiet --timings: –timeings 参数可以生成编译依赖的各 crate 的耗时cargo run: 编译和运行默认 binary(src/main.rs), 可以通过 –bin 来指定要运行的 binary name;cargo cache: 分析和清理全局 cache(~/.cargo);cargo update: 更新 Cargo.lock 文件;cargo doc --open: 浏览器查看项目文档rustup doc --std: 查看 Rust 标准库文档以及其它离线文档;
cargo +nightly build: 使用指定的 toolchain,如+stable, +esp, +nightly
cargo new 默认为项目创建 .git 目录,可以使用 --vcs none 关闭;
查看 cargo 调用的 rustc 参数: cargo build --verbose
查看 rustc 调用的外部命令(如系统链接器 ld,交叉编译器 gcc 或 clang 等)参数:cargo build --config 'build.rustflags=["--print", "link-args"]'
使用 nightly rustc 的 -Zunpretty=expanded 参数来展开宏:https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/43364
cargo +nightly build --config 'build.rustflags=["--print", "link-args", "-Z", "unpretty=expanded"]'cargo +nightly rustc -- -Zunpretty=expanded
rustup doc:本地查看标准库、cargo、The Book 等文档 #
❯ rustup doc --help
Open the documentation for the current toolchain
Usage: rustup[EXE] doc [OPTIONS] [TOPIC]
Arguments:
[TOPIC] Topic such as 'core', 'fn', 'usize', 'eprintln!', 'core::arch', 'alloc::format!', 'std::fs', 'std::fs::read_dir', 'std::io::Bytes', 'std::iter::Sum', 'std::io::error::Result'
etc...
Options:
--path Only print the path to the documentation
--toolchain <TOOLCHAIN> Toolchain name, such as 'stable', 'nightly', or '1.8.0'. For more information see `rustup help toolchain`
--alloc The Rust core allocation and collections library
--book The Rust Programming Language book
--cargo The Cargo Book
--clippy The Clippy Documentation
--core The Rust Core Library
--edition-guide The Rust Edition Guide
--embedded-book The Embedded Rust Book
--error-codes The Rust Error Codes Index
--nomicon The Dark Arts of Advanced and Unsafe Rust Programming
--proc_macro A support library for macro authors when defining new macros
--reference The Rust Reference
--rust-by-example A collection of runnable examples that illustrate various Rust concepts and standard libraries
--rustc The compiler for the Rust programming language
--rustdoc Documentation generator for Rust projects
--std Standard library API documentation
--style-guide The Rust Style Guide
--test Support code for rustc's built in unit-test and micro-benchmarking framework
--unstable-book The Unstable Book
-h, --help Print help
Discussion:
Opens the documentation for the currently active toolchain with
the default browser.
By default, it opens the documentation index. Use the various
flags to open specific pieces of documentation.
cargo 向 rustc 传参的方式 #
cargo rustc [options] [-- args]: 编译当前 package(opstions 部分指定 cargo 参数,如-p/–lib/–bin 等),--后的args为传递给 rustc 的编译器参数;
cargo rustc --lib -- -Z print-type-sizescargo rustc --lib -- --crate-type lib,cdylib
- 通过环境变量
RUSTFLAGS配置 rustc 编译器参数:
RUSTFLAGS="-C linker=./gcc-print.sh -C link-self-contained=yes" cargo build --target=aarch64-unknown-linux-musl
- 通过 cargo 的
--config参数,可配置的参数为.cargo/config.toml文件中的内容:
cargo build --config 'build.rustflags=["--print", "link-args"]'
rustc unstable 的选项 (-Zkey=value) 默认需要使用 +nightly 版本的 toolchain 才能看到和使用:
# stable rustc 没有 -Z 选项
❯ rustc --help -v |grep -- -Z
$ rustc +nightly --help -v |grep -- -Z
-Z help Print unstable compiler options
# 查看 -Z 支持的选项
$ rustc +nightly -Z help |head
Available options:
-Z allow-features=val -- only allow the listed language features to be enabled in code (comma separated)
-Z always-encode-mir=val -- encode MIR of all functions into the crate metadata (default: no)
-Z annotate-moves=val -- emit debug info for compiler-generated move and copy operations to make them visible in profilers. Can be a boolean or a size limit in bytes (default: disabled)
-Z assert-incr-state=val -- assert that the incremental cache is in given state: either `loaded` or `not-loaded`.
-Z assume-incomplete-release=val -- make cfg(version) treat the current version as incomplete (default: no)
-Z autodiff=val -- a list of autodiff flags to enable
通过指定 RUSTC_BOOTSTRAP=1 环境变量,也可以在 stable toolchain 使用这些 unstable 特性:
❯ RUSTC_BOOTSTRAP=1 rustc --help -v |grep -- -Z
-Z help Print unstable compiler options
打印 rustc 编译耗时的 profile:
RUSTC_BOOTSTRAP=1 cargo rustc --release -- -Z self-profile
# cargo chef:
RUSTC_BOOTSTRAP=1 RUSTFLAGS='-Zself-profile' cargo chef cook --release ...
# final build:
RUSTC_BOOTSTRAP=1 RUSTFLAGS='-Zself-profile' cargo build --release ...
Package 布局 #
Cargo.toml/Cargo.lock:位于 package root 目录下。cargo update命令更新 Cargo.lock 文件;- 源码:位于
src目录下:- 缺省 lib 文件:src/lib.rs。对于目录类型的 module,则需要在目录中创建 mod.rs 文件。
- 缺省 binary 文件:src/main.rs
- 其他 binary 文件,src/bin/xxx.rs
- Benchmarks: 位于 benches 目录;
- 示例: 位于 examples 目录;
- 集成测试:位于 tests 目录;
bin/examples/tests/benches 目录下的各文件都会被编译为 单独的可执行的二进制。支持目录形式的二进制:目录下必须有 main.rs 文件以及依赖的 module 文件。
.
├── Cargo.lock
├── Cargo.toml
├── src/
│ ├── lib.rs
│ ├── main.rs # binary name 为 Cargo.toml 中的 package name,需要使用 use create::xx 或 use create_name:: 来应用 lib.rs 中的
│ └── bin/
│ ├── named-executable.rs # binary name 为文件名
│ ├── another-executable.rs
│ └── multi-file-executable/ # binary 也可以是目录,binary name 为目录名,目录下需要有 main.rs 文件。
│ ├── main.rs
│ └── some_module.rs # binary 依赖的 module
├── benches/
│ ├── large-input.rs
│ └── multi-file-bench/
│ ├── main.rs
│ └── bench_module.rs
├── examples/
│ ├── simple.rs
│ └── multi-file-example/
│ ├── main.rs
│ └── ex_module.rs
└── tests/
├── some-integration-tests.rs
└── multi-file-test/
├── main.rs
└── test_module.rs
cargo test #
cargo test [name] 运行单元或集成测试,它搜索两个地方:
- src/ 目录下各源码文件,包含单元测试和文档测试;
- tests/ 目录下的集成测试文件,需要 import 当前 crate 到 tests 下的文件中;
[name] 对应 tests 下的文件名或目录名,或对应 src 中 #[test] 对应的函数名关键字。
target 目录(Build Cache)和 Profile #
cargo build 将输出内容保存到 root workspace 下的 target 目录, 该目录也是项目的 Build Cache。
可以 by workspace 或 package 来设置 Build Cache 目录:
- 环境变量:
CARGO_TARGET_DIR - 配置参数:
build.target-dir - 命令行选项:
--target-dir
target 目录布局取和 --target 参数有关系:
- 如果指定了
--target(可以有多个),则生成的目录结构:
- target/
/debug/: 如 target/thumbv7em-none-eabihf/debug/ - target/
/release/: 如 target/thumbv7em-none-eabihf/release/
- 如果没有指定
--target,则表示构建 host arch(使用rustup show命令查看),构建结果保存到target/<profile>目录下。
Cargo 内置了 4 个 <profile>:dev(默认), test, release, bench,根据命令行参数自动选择,也可以自定义:
- dev 和 test profile 结果保存到
target/debug/目录:默认,使用--debug选项指定; - release 和 bench profile 结果保存到
target/release/目录:使用--release选项指定; - 自定义的 foo profile 结果保存到
target/foo/目录:使用--profile=foo选项指定;
各类型 profile 对应的参数可以在 Cargo.toml 文件中进行 配置 ,如指定优化级别,是否包含符号表等,具体参考后文 Profile 一节。
target/<profile> 下的目录含义(以 debug 为例):
- target/debug/:构建后的二进制和库文件;
- target/debug/examples/:构建后的例子。
- target/debug/deps/:依赖项等。
- target/debug/incremental/:rustc 增量输出,用于加速后续构建的缓存。
- target/debug/build/:来自
build scripts(build.rs)的输出。 - target/doc/: 来自
cargo doc的输出; - target/package/:来自
cargo package和cargo publish的输出。
在 target/<profile> 目录下以 .d 结尾的文件为 dep-info,它们风格类似于 Makefile,包含 binary/lib 依赖的文件:
❯ ls -l target/debug/*.d
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 263 Nov 20 21:19 target/debug/delete_post.d
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 257 Nov 20 21:18 target/debug/get_post.d
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 265 Nov 20 21:17 target/debug/publish_post.d
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 261 Nov 27 19:27 target/debug/show_posts.d
-rw-r--r-- 1 alizj 261 Nov 20 21:05 target/debug/write_post.d
❯ head target/debug/get_post.d
/Users/alizj/code/rust/diesel_demo/target/debug/get_post: /Users/alizj/code/rust/diesel_demo/src/bin/get_post.rs /Users/alizj/code/rust/diesel_demo/src/lib.rs /Users/alizj/code/rust/diesel_demo/src/models.rs /Users/alizj/code/rust/diesel_demo/src/schema.rs
Cargo.toml 文件 #
Cargo 支持两种 by 项目的配置:
.cargo/config.toml: 配置 cargo 调用 rustc 相关的参数;Cargo.toml: 也称为 manifest 文件,可以引用 config.toml 中的配置,如 registry;
.cargo/config.toml 的配置参数可以使用 --config 参数重定义,如 cargo build --config 'build.rustflags=["--print", "link-args"]'
还可以 by 项目创建 rust-toolchain.toml 文件,用来指定该项目要安装和使用的 toolchain 版本,要编译的 targets 列表,要下载的 components 列表等。
Cargo.toml 配置参数 #
参考:https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
示例:
[package]
name = "hello_world"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["Alice <[email protected]>", "Bob <[email protected]>"]
edition = '2021' # 影响所有 package/test/bens/examples,默认为 2015
rust-version = "1.56" # 兼容的 rustc 编译器版本
description = "A short description of my package"
documentation = "https://docs.rs/bitflags"
readme = "README.md"
homepage = "https://serde.rs/"
repository = "https://github.com/rust-lang/cargo/"
license = "MIT OR Apache-2.0"
license-file = "LICENSE.txt"
keywords = ["gamedev", "graphics"
categories = ["command-line-utilities", "development-tools::cargo-plugins"]
# 所属的 workspace,适用于不存在 wrokspace root 目录的情况。
workspace = "path/to/workspace/root"
# 构建脚本路径
build = "build.rs"
# 要链接到的 native lib 名称,如linux 平台的 git2 表示 libgit2.a。
links = "git2"
# 发布到 crates.io 上包含和忽略的文件,如果 build script 没有输出 rerun-if-* 则也用于跟踪是否需要重新执行 build script;
exclude = ["/ci", "images/", ".*"]
include = ["/src", "COPYRIGHT", "/examples", "!/examples/big_example"]
# 或者 false
publish = ["some-registry-name"]
# 当 package 有多个 binary 时(如 src/bin/a.rs 和 src/bin/b.rs),指定 cargo run 默认编译运行的 binary
default-run = "a"
# package.metadata 会被 cargo 忽略,而为从 Cargo.toml 中读取配置信息的其它工具使用。
[package.metadata.android]
package-name = "my-awesome-android-app"
assets = "path/to/static"
# lint 对本地 package 而非 dependencies 进行检查
[lints.rust] # rustc lint
unsafe_code = "forbid" # 等效于 unsafe_code = { level = "forbid", priority = 0 }
[lints.clippy] # clippy lint
enum_glob_use = "deny"
[badges]
# The `maintenance` table indicates the status of the maintenance of
# the crate. This may be used by a registry, but is currently not
# used by crates.io. See https://github.com/rust-lang/crates.io/issues/2437
# and https://github.com/rust-lang/crates.io/issues/2438 for more details.
# 编译构建依赖
[dependencies]
# test、bench、example 依赖
[dev-dependencies]
# 构建脚本 build.rs 和 proc-mecro 依赖
[build-dependencies]
# target 依赖,可以使用 cfg!() 条件包含
[target.*.dependencies]
# 为编译器提供各种优化和调试的参数集合
[profile.*]
# 一个 package 只能有一个 lib,根默认为 src/lib.rs,但是可以有多个 bin/example/test/bench
# 所以 [lib] 不是列表,而 [[bin]]/[[bench]]/[[test]] 等是列表。
#
# 根 lib 配置,默认 path 是 src/lib.rs, name 默认是 package name;
# 可以通过 [lib].name 来重命名,重新指定 path。
#
# path: 未指定时, 根据 section 自动推导;
# doctest: 只对 lib 有效, 指定 cargo test 是否执行 doc example
# bench: 是否对指定的 target 搜索和执行 bench, 对于 bins/libs/bench 默认为 true
# proc-macro: 只对 lib 有效; 指定该 lib 为 proc-macro crate 类型
# crate-type: 可选值 bin/lib/rlib/dylib/cdylib/staticlib/proc-macro
# 只能对 [lib] 和 [[example]] 配置 crate-type。
# 对于 bin/test/bench,默认只能为 bin。
# required-features: 对于 lib 外的其他 target 有效, 表示只有启动对应 feature 时才build 该 target。
[lib]
name = "foo" # The name of the target. 默认是 crate name
path = "src/lib.rs" # The source file of the target.
test = true # Is tested by default.
doctest = true # Documentation examples are tested by default.
bench = true # Is benchmarked by default.
doc = true # Is documented by default.
plugin = false # Used as a compiler plugin (deprecated).
proc-macro = false # Set to `true` for a proc-macro library.
harness = true # Use libtest harness.
edition = "2015" # The edition of the target.
crate-type = ["lib"] # The crate types to generate.
required-features = [] # Features required to build this target (N/A for lib).
## 一个 package 可以有多个 binary,默认是:src/main.rs 和 src/bin/*.rs
## src/main.rs binary 的 name 和 package name 一致,可以通过 [[bin]].name 来重命名,后续可以使用 --bin name 来指定这里的 name。
## bin 可以有多个,所以 [[bin]] 是个列表
#
# binary 可以使用 crate 的 pub API,编译使用 [dependencies] 配置。
# 使用 cargo run --bin <bin-name> 来指定。
# cargo install --bin <bin-name> 安装到 ~/.cargo/bin 目录下。
[[bin]] # [[xx]] 表示是一个列表,可以重复指定多个
name = "cool-tool" # 重命名 path 对应的 bin 名称
path = "src/main.rs" # 未指定时默认为 src/main.rs
test = false
bench = false
crate-type = ["bin"] # 对于 bin,默认为 bin, 而且只能为 bin
[[bin]]
name = "frobnicator"
required-features = ["frobnicate"]
# example 列表, 各 example 可执行程序文件位于 examples 目录下, 编译后位于
# target/debug/examples 目录下, 使用 [dependencies] 和 [dev-dependenceis] 中的配置。
#
# example 是可执行的 binary(有 main() 函数),可以通过 crate-type = ["staticlib"] 将它编译为库。
#
# example 相关命令: cargo build/run/install --example <example-name>
# cargo test 默认只编译 examples 但不运行, 可以为 example 设置 test=ture 来在 test 时运行 example。
[[example]]
name = "foo"
crate-type = ["staticlib"]
# test 列表, 分为 src/ 下的单元测试和 tests 下的集成测试(只能使用 crate 公共 APIs), 为一个可执行程序。默认并行执行 tests。
# 集成测试程序使用 [dependencies] 和 [dev-dependenceis] 中的配置。
[[test]]
# bench 列表, 位于 src/ 或 benches 目录下的单独可执行程序, 使用 #[bench] 来修饰, 使用 cargo bench 来执行。
[[bench]]
[workspace]
crate type #
Rust crate 的类型如下:
- 用于 Rust crate 之间链接的 Rust 库格式类型:
-
lib— Generates a library kind preferred by the compiler,currently defaults to rlib.- 默认的 crate type 类型,实际指向
rlib;
- 默认的 crate type 类型,实际指向
-
rlib— A Rust static library.- 即 Rust 静态库格式,文件名为
*.rlib,可以被其它 crate 链接; - 它打包了本 crate 以及它依赖的其它 upstream crate(不含 Rust 标准库);
- 如果要链接外部语言库,则只能使用静态的外部库,否则会打印警告;
- 即 Rust 静态库格式,文件名为
-
dylib— A Rust dynamic library.- 即 Rust 动态库格式,可以被其它 crate 链接;
- 用于将 Rust crate 及其依赖(含 Rust 标准库)打包为系统库格式,供其它 C/C++ 程序链接:
-
staticlib— A native static library.- 即系统静态库格式,linux 系统的文件名为 *.a
- staticlib 不可以被其它 Rust crate 链接,它的主要功能是将 Rust crate 及其依赖(包含 Rust 标准库)打包到
*.a静态库中,从而可以被其它语言如 C/C++ 的程序进行链接。 - 该 *.a 本身可能有动态库依赖,在链接该 *.a 时也需要链接这些动态库,可以使用
--print=native-static-libs打印。
-
cdylib— A native dynamic library.- 即系统动态库格式,linux 系统的文件名为 *.so
- 和 staticlib 类似,也是将 Rust crate 及其依赖打包到
*.so动态库中,从而可以被其它语言如 C/C++ 的程序进行链接。
- ELF 可执行程序类型,以及 proc-macro 类型
- bin — A runnable executable program.
- proc-macro — Generates a format suitable for a procedural macro library that may be loaded by the compiler.
lib、rlib、dylib 是 Rust 编译器识别和使用的 Rust 自己的静态库和动态库格式,Rust crate 只有生成这三种库格式后,才能被其它 Rust crate 链接:
staticlib 和 cdylib 是将 Rust 代码打包到系统库类型文件中,然后被其它语言的程序链接(不能被其它 Rust crate 链接)。
- 它会将该 Rust 及依赖的其它 crate 和 Rust 标准库都打包到生成的 staticlib 或 cdynlib 中,从而可以被 C/C++ 程序链接。
- 由于 rustc 默认会对导出符号名称进行 mangle,所以为了让 C/C 程序能正确链接符号,在 Rust 代码中需要对导出的符号使用
#[no_mangle]
对于 Cargo 项目,cargo 在调用 rustc 时默认设置的 crate type 如下:
- src/lib.rs 默认为 lib,它是 rlib 的别名,即 Rust 静态库格式。
- src/main.rs、src/bin/*.rs、以及 tests、benches、examples 默认为 bin,这些文件只能为 bin 类型(不能变更);
对于 src/lib.rs,它们的 crate type 可以通过 Cargo.toml 的 [lib].crate-type 参数来配置,如 bin, lib, rlib, dylib, cdylib, staticlib, and proc-macro
源码中可以使用宏来指定 crate type:#![crate_type = "bin"]。
在编译 lib 类型 crate 时,可以通过 rustc 的 --crate-type 参数来指定生成的 库文件类型。
$ cargo rustc --lib -- -Z print-type-sizes
$ cargo rustc --lib --crate-type lib,cdylib
参考:
- https://doc.rust-lang.org/rustc/command-line-arguments.html?highlight=bundle#--crate-type-a-list-of-types-of-crates-for-the-compiler-to-emit
- https://doc.rust-lang.org/reference/linkage.html
- https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/cargo-targets.html
Rust 编译结果分析 #
rlib #
一个测试 crate:
// src/lib.rs
// 需要是 pub,这样才会在生成的 rlib 中包含输出。
pub fn hello() {
println!("hello!");
}
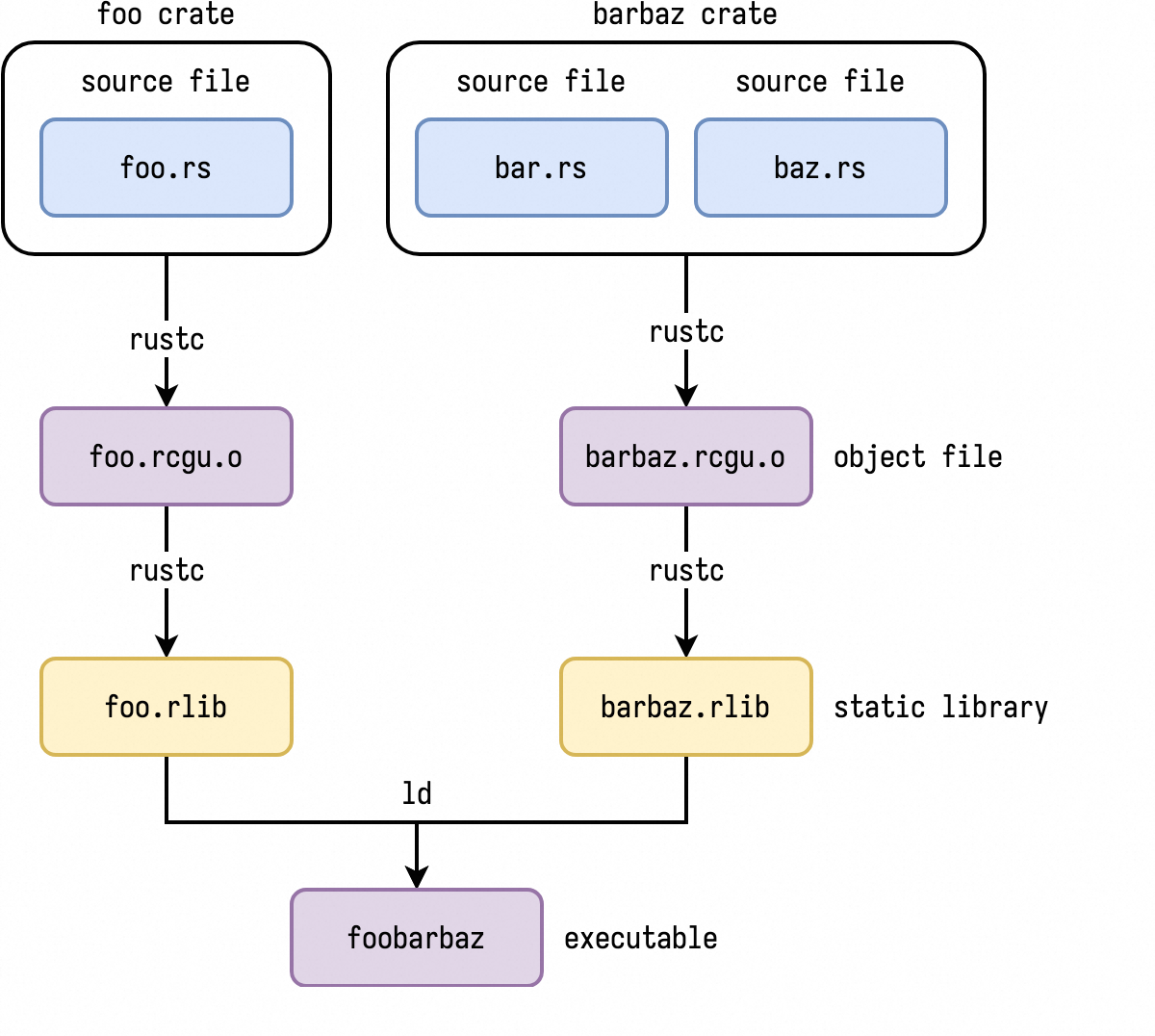
cargo build 默认生成 rlib 库:
- 它实际是 ar 格式,即 object 文件的集合;
- nm 可以打印 rlib 中的符号,需要进行 demangle 后(可以使用 rustfilt 或 nm –demangle 命令)才能看到真实的符号名称;
- rlib 打包了 crate 及其依赖的 crate 的所有对象文件;
rustc 编译 crate 的过程:
- 将 foo.rs 编译为 foo.rcgu.o 对象文件;(RCGU:Rust Code Gen Unit)
- 将 crate 的多个 *.rs 文件的 *.rcgu.o 文件打包到一个 rlib 文件中。
- 将 binary crate 和依赖的多个 crate 的 rlib 文件链接到一起,形成 binary;
rlib 生成的顺序:
❯ cargo build # 或者 cargo rustc --lib
# --timeings 参数可以生成编译依赖的各 crate 的耗时
> cargo clean && cargo build --release --quiet --timings
❯ find target/ -type f -name '*.rlib'
target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.rlib
target/debug/libmy_demo.rlib
❯ file target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.rlib
target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.rlib: current ar archive
❯ ar t target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.rlib
__.SYMDEF
lib.rmeta
my_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.6fg39t3e0vwd88d9zbr7ioa1j.1y07x8w.rcgu.o
my_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.aq8mw1jgqf27i1b4p5k0bzldz.1y07x8w.rcgu.o
❯ nm target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.rlib
lib.rmeta:
target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.rlib:lib.rmeta: no symbols
my_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.6fg39t3e0vwd88d9zbr7ioa1j.1y07x8w.rcgu.o:
U __ZN3std2io5stdio6_print17h068a7c8fe03701f4E
U __ZN4core3fmt2rt38_$LT$impl$u20$core..fmt..Arguments$GT$9new_const17ha3888ccef9b469abE
0000000000000000 T __ZN7my_demo5hello17h4b85738f5c82ab0fE
0000000000000034 s l_anon.b27ae52ee22afa02c25801ca93529f61.0
0000000000000040 s l_anon.b27ae52ee22afa02c25801ca93529f61.1
0000000000000000 t ltmp0
0000000000000034 s ltmp1
0000000000000040 s ltmp2
00000000000000ca s ltmp3
0000000000000298 s ltmp4
00000000000002b8 s ltmp5
my_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.aq8mw1jgqf27i1b4p5k0bzldz.1y07x8w.rcgu.o:
0000000000000000 T __ZN4core3fmt2rt38_$LT$impl$u20$core..fmt..Arguments$GT$9new_const17ha3888ccef9b469abE
0000000000000048 s l_anon.d56747e2a7f22d5a93d4373863465371.0
0000000000000000 t ltmp0
0000000000000048 s ltmp1
0000000000000635 s ltmp2
0000000000001020 s ltmp3
0000000000001040 s ltmp4
# 使用 rustfilt 对 rust 符号进行 demangle
❯ nm target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.rlib | rustfilt
target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.rlib:lib.rmeta: no symbols
lib.rmeta:
my_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.6fg39t3e0vwd88d9zbr7ioa1j.1y07x8w.rcgu.o:
U _std::io::stdio::_print
U _core::fmt::rt::<impl core::fmt::Arguments>::new_const
0000000000000000 T _my_demo::hello
0000000000000034 s l_anon.b27ae52ee22afa02c25801ca93529f61.0
0000000000000040 s l_anon.b27ae52ee22afa02c25801ca93529f61.1
0000000000000000 t ltmp0
0000000000000034 s ltmp1
0000000000000040 s ltmp2
00000000000000ca s ltmp3
0000000000000298 s ltmp4
00000000000002b8 s ltmp5
my_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.aq8mw1jgqf27i1b4p5k0bzldz.1y07x8w.rcgu.o:
0000000000000000 T _core::fmt::rt::<impl core::fmt::Arguments>::new_const
0000000000000048 s l_anon.d56747e2a7f22d5a93d4373863465371.0
0000000000000000 t ltmp0
0000000000000048 s ltmp1
0000000000000635 s ltmp2
0000000000001020 s ltmp3
0000000000001040 s ltmp4
# 也使用 nm --demangle 来对 lib 中的 rust 符号进行 demangle
❯ nm --demangle target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-2c918bd8bd6b1c77.rlib
dylib #
编译生成 dylib 类型:
- dylib 是 Rust 自身的标准库格式,实际是 ELF 文件类型;
- 可以使用 objdump 打印其中的符号表,并进行 demangle
❯ cargo rustc --lib -- --crate-type dylib
❯ ls target/debug/
build/ deps/ examples/ incremental/ libmy_demo.d libmy_demo.rlib
❯ ls -l target/debug/deps/
total 1.5M
-rwxr-xr-x 1 zj 1.5M Jul 4 11:14 libmy_demo-1752cfb8404360eb.dylib*
-rw-r--r-- 1 zj 12K Jul 4 11:14 libmy_demo-1752cfb8404360eb.rlib
-rw-r--r-- 1 zj 2.5K Jul 4 11:14 libmy_demo-1752cfb8404360eb.rmeta
-rw-r--r-- 2 zj 2.7K Jul 4 11:14 my_demo-1752cfb8404360eb.6fg39t3e0vwd88d9zbr7ioa1j.07hj7xi.rcgu.o
-rw-r--r-- 2 zj 5.9K Jul 4 11:14 my_demo-1752cfb8404360eb.aq8mw1jgqf27i1b4p5k0bzldz.07hj7xi.rcgu.o
-rw-r--r-- 1 zj 388 Jul 4 11:14 my_demo-1752cfb8404360eb.d
# 生成了动态库 dylib 库文件
❯ file target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-1752cfb8404360eb.dylib
target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-1752cfb8404360eb.dylib: Mach-O 64-bit dynamically linked shared library arm64
❯ objdump --syms target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-1752cfb8404360eb.dylib |rustfilt |wc -l
11309
❯ objdump --syms target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-1752cfb8404360eb.dylib |rustfilt |head
target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-1752cfb8404360eb.dylib: file format mach-o arm64
SYMBOL TABLE:
0000000000000958 l F __TEXT,__text _<alloc::collections::btree::map::Iter<K,V> as core::iter::traits::iterator::Iterator>::next
0000000000000a94 l F __TEXT,__text _<T as core::any::Any>::type_id
0000000000000ac4 l F __TEXT,__text _<T as core::any::Any>::type_id
0000000000000af4 l F __TEXT,__text _<T as core::any::Any>::type_id
0000000000000b24 l F __TEXT,__text _<bool as core::fmt::Debug>::fmt
0000000000000b34 l F __TEXT,__text _<&T as core::fmt::Debug>::fmt
staticlib #
编译生成 staticlib 类型:
- staticlib 是系统静态库(*.a) 类型;
- 它打包了 crate 及依赖的 crate 的所有符号(包含 Rust 标准库),可以被其它 C/C++ 程序链接;
- 由于 rustc 默认会对导出符号名称进行 mangle,所以为了让 C/C 程序能正确链接符号,在 Rust 代码中需要对导出的符号使用
#[no_mangle]
❯ cargo rustc --lib -- --crate-type staticlib
❯ ls target/debug/
build/ deps/ examples/ incremental/ libmy_demo.d libmy_demo.rlib
❯ ls -l target/debug/deps/
total 16M
-rw-r--r-- 1 zj 16M Jul 4 11:17 libmy_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.a
-rw-r--r-- 1 zj 12K Jul 4 11:17 libmy_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.rlib
-rw-r--r-- 1 zj 2.5K Jul 4 11:17 libmy_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.rmeta
-rw-r--r-- 2 zj 2.7K Jul 4 11:17 my_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.6fg39t3e0vwd88d9zbr7ioa1j.14m2vgu.rcgu.o
-rw-r--r-- 2 zj 5.9K Jul 4 11:17 my_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.aq8mw1jgqf27i1b4p5k0bzldz.14m2vgu.rcgu.o
-rw-r--r-- 1 zj 384 Jul 4 11:17 my_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.d
❯ ar t target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.a |head
__.SYMDEF
my_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.6fg39t3e0vwd88d9zbr7ioa1j.14m2vgu.rcgu.o
my_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.aq8mw1jgqf27i1b4p5k0bzldz.14m2vgu.rcgu.o
my_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.am4vmyp6gsgp9crfpou4ngk1b.14m2vgu.rcgu.o
std-af0f282b96954ac9.std.72c7846bd0c5b2df-cgu.0.rcgu.o
panic_unwind-eafbb5ea5df11687.panic_unwind.29942598dde052fe-cgu.0.rcgu.o
object-091f97e9f7b1e9a0.object.63ce0cc8faeaeb20-cgu.0.rcgu.o
memchr-89dd1b3eaceaf16a.memchr.9fc0d4dd789ae0d1-cgu.0.rcgu.o
addr2line-9be47fa9e342462b.addr2line.b61a8a1856850aac-cgu.0.rcgu.o
gimli-3ecc0aa72e38a2f0.gimli.9346c6a51b682f64-cgu.0.rcgu.o
❯ ar t target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.a |wc -l
380
❯ nm --demangle target/debug/deps/libmy_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.a |head -20
my_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.6fg39t3e0vwd88d9zbr7ioa1j.14m2vgu.rcgu.o:
U std::io::stdio::_print::h068a7c8fe03701f4
U core::fmt::rt::_$LT$impl$u20$core..fmt..Arguments$GT$::new_const::ha3888ccef9b469ab
0000000000000000 T my_demo::hello::h4b85738f5c82ab0f
0000000000000034 s l_anon.b27ae52ee22afa02c25801ca93529f61.0
0000000000000040 s l_anon.b27ae52ee22afa02c25801ca93529f61.1
0000000000000000 t ltmp0
0000000000000034 s ltmp1
0000000000000040 s ltmp2
00000000000000ca s ltmp3
0000000000000298 s ltmp4
00000000000002b8 s ltmp5
my_demo-6c6f35ce0e39f05f.aq8mw1jgqf27i1b4p5k0bzldz.14m2vgu.rcgu.o:
0000000000000000 T core::fmt::rt::_$LT$impl$u20$core..fmt..Arguments$GT$::new_const::ha3888ccef9b469ab
0000000000000048 s l_anon.d56747e2a7f22d5a93d4373863465371.0
0000000000000000 t ltmp0
0000000000000048 s ltmp1
0000000000000635 s ltmp2
参考:
- https://fasterthanli.me/articles/why-is-my-rust-build-so-slow
- https://sharnoff.io/blog/why-rust-compiler-slow
编译依赖 dependencies #
依赖来源可以是:
- crates.io
- git
- 本地 path
对于 git 和 本地 path 来源类型,version 是可选的,但如果指定,则必须要匹配。
[dependencies]
time = "0.1.12" # 表示等效版本: >=0.1.12, <0.2.0,后续 cargo update 时会自动更新升级版本
log = "^1.2.3" # 表示严格使用 "1.2.3" 版本
# 各种等效版本情况
1.2.3 := >=1.2.3, <2.0.0
1.2 := >=1.2.0, <2.0.0
1 := >=1.0.0, <2.0.0
0.2.3 := >=0.2.3, <0.3.0
0.2 := >=0.2.0, <0.3.0
0.0.3 := >=0.0.3, <0.0.4
0.0 := >=0.0.0, <0.1.0
0 := >=0.0.0, <1.0.0
~1.2.3 := >=1.2.3, <1.3.0
~1.2 := >=1.2.0, <1.3.0
~1 := >=1.0.0, <2.0.0
* := >=0.0.0
1.* := >=1.0.0, <2.0.0
1.2.* := >=1.2.0, <1.3.0
>= 1.2.0
> 1
< 2
= 1.2.3
>= 1.2, < 1.5
指定 git 来源:
# 自定义 registry,指定的 registry 必须在 .cargo/config.tmol 中配置
some-crate = { version = "1.0", registry = "my-registry" }
# 使用最新提交
regex = { git = "https://github.com/rust-lang/regex.git" }
# 指定 branch/tag/rev
regex = { git = "https://github.com/rust-lang/regex.git", branch = "next" }
regex = { git = "https://github.com/rust-lang/regex.git", rev = "4c59b707" }
# rev 格式
rev = "refs/pull/493/head"
rev = "4c59b707"
指定本地目录来源:
# 在 hello_world pacakge 目录下创建 hello_utils package
$ cargo new hello_utils
# hello_world/Cargo.toml
[dependencies]
hello_utils = { path = "hello_utils" }
hello_utils = { path = "hello_utils", version = "0.1.0" }
平台相关依赖(可以使用 cfg() 函数):
[target.x86_64-pc-windows-gnu.dependencies]
winhttp = "0.4.0"
[target.i686-unknown-linux-gnu.dependencies]
openssl = "1.0.1"
[target.'cfg(windows)'.dependencies]
winhttp = "0.4.0"
[target.'cfg(unix)'.dependencies]
openssl = "1.0.1"
[target.'cfg(target_arch = "x86")'.dependencies]
native-i686 = { path = "native/i686" }
[target.'cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")'.dependencies]
native-x86_64 = { path = "native/x86_64" }
这里的 cfg() 不支持使用可选 feature 来指定依赖,如 [target.'cfg(feature="fancy-feature")'.dependencies],但可以使用 [features] 机制。
测试依赖 dev-dependencies #
在编译 tests/examples/benchs 时使用,不会被传递到依赖它的 package:
[dev-dependencies]
tempdir = "0.3"
[target.'cfg(unix)'.dev-dependencies]
mio = "0.0.1"
构建脚本依赖 build-dependencies #
在编译构建脚本(build script,build.rs) 或 proc macro 时使用。
编译构建脚本使用 build-dependencies,而不是 dependencies/dev-dependenices,是因为构建脚本和 package 源码是分开编译的:先编译构建脚本或 proc-macro 然后再编译 package。
# build script/proc macro 及其依赖
[build-dependencies]
cc = "1.0.3"
[target.'cfg(unix)'.build-dependencies]
cc = "1.0.3"
开启依赖 package 的 features #
[dependencies]
# 启用 default-features 和 features 列表中的 feature
serde = { version = "1.0.118", features = ["derive"] }
[dependencies]
# 不启用 default feature,启用指定的 feature 列表
awesome = { version = "1.3.5", default-features = false,features = ["secure-password", "civet"]}
# 等效于
[dependencies.awesome]
version = "1.3.5"
default-features = false
features = ["secure-password", "civet"]
重命名依赖 package #
使用 package 参数来指定实际的 package 名称,适用于同时依赖同一个 package 的不同版本、不同位置:
[package]
name = "mypackage"
version = "0.0.1"
[dependencies]
foo = "0.1"
# package 指定实际的 package 名称
bar = { git = "https://github.com/example/project.git", package = "foo" }
baz = { version = "0.1", registry = "custom", package = "foo" }
# 后续代码使用
# use foo; // crates.io
# use bar; // git repository
# use baz; // registry `custom`
对于可选依赖,也支持重命名:
[dependencies]
# 可选依赖,重命名为 bar
bar = { version = "0.1", package = 'foo', optional = true }
[features]
# 开启该可选依赖,并开启 log-debug 特性。
log-debug = ['bar/log-debug']
继承 workspace 的依赖 #
member package 可以指定某个依赖配置继承自 workspace(workspace=true),对于该继承的依赖项只能配置 features 和 optional 参数:
- 可以指定 member package 的 dependencies、build-dependencies、dev-dependencies 中的依赖 package 继承自 workspace。
# [PROJECT_DIR]/Cargo.toml
[workspace]
members = ["bar"]
# workspace 级别定义的依赖
[workspace.dependencies]
cc = "1.0.73"
rand = "0.8.5"
regex = { version = "1.6.0", default-features = false, features = ["std"] }
# worksapce 成员 Package
# [PROJECT_DIR]/bar/Cargo.toml
[package]
name = "bar"
version = "0.2.0"
[dependencies]
# workspace=true 表示继承 workspace 的依赖配置,这时只能指定 features/optional 两个配置参数。
regex = { workspace = true, features = ["unicode"] } # 在 workspace features 的基础上额外增加 unicode feature
[build-dependencies]
cc.workspace = true
[dev-dependencies]
rand.workspace = true
patch 依赖 #
replace 语法已经被抛弃,建议使用 patch。
[package]
name = "my-library"
version = "0.1.0"
[dependencies]
uuid = "1.0"
# 后续可以使用 patch 对 dependencies 中指定的 package 参数进行修改
[patch.crates-io] # crates-io:指定包的索引仓库
# 使用本地的 uuid,未指定 version 时使用前面指定的 1.0 版本;
uuid = { path = "../path/to/uuid" }
# 或者,使用 git 的 uuid
uuid = { git = 'https://github.com/uuid-rs/uuid.git' }
后续使用 my-library package 的其他代码也需要指定同样的 patch,如:
[package]
name = "my-binary"
version = "0.1.0"
[dependencies]
my-library = { git = 'https://example.com/git/my-library' }
uuid = "1.0"
[patch.crates-io]
uuid = { git = 'https://github.com/uuid-rs/uuid.git' }
除了来源于 cartes-io 的 package 外,也可以 patch 自定义 registry 的 package:
[patch."https://github.com/your/repository"]
my-library = { path = "../my-library/path" }
多版本 patch:
[patch.crates-io]
serde = { git = 'https://github.com/serde-rs/serde.git' }
serde2 = { git = 'https://github.com/example/serde.git', package = 'serde', branch = 'v2' }
其它例子:
[dependencies.baz]
git = 'https://github.com/example/baz.git'
[patch.'https://github.com/example/baz']
baz = { git = 'https://github.com/example/patched-baz.git', branch = 'my-branch' }
config.toml paths 重载 #
如果不想通过 Cargo.toml 的 [patch] 来修改依赖参数,也可以在项目的 .cargo/config.toml 中通过 paths 来指定要重载的 package:
paths = ["/path/to/uuid"] # 数组指向包含 Cargo.toml 的 package 目录
features #
feature 提供了一种条件编译和可选依赖的机制。
在 Cargo.toml 的 [features] 中定义一系列 feature。
[features]
# 定义一个 webp feature,它不依赖(启用)其它 feature。
webp = []
在命令行 cargo build --features "fa fb" 来启用 feature 列表。
cargo --features "fa fb"会被转换为rustc --cfg参数, 如--cfg 'feature="fa" feature="fb"';
也可以在 [dependencies] 中为依赖的 package 启用 feature 列表。
[dependencies]
# 不启用 default feature,启用指定的 feature 列表
awesome = { version = "1.3.5", default-features = false,features = ["secure-password", "civet"]}
代码中可以通过 cfg!() 宏来判断该 feature 是否被启用, 从而实现条件编译:
#[cfg(feature = "webp")]
pub mod webp;
在定义 feature 时,feature 名不能和 dependencies 列表中的 package 名重复,这是由于如果依赖的 package 为 optional 时, cargo 会自动创建一个同名的 feature。
默认定义的 feature 都是未启用状态, 可以 使用 default 来指定默认启用的 features。
- 在 build 时, 不管是否指定
--features, 默认都会启用 default feature; - 通过
cargo --no-default-features来关闭; - 在声明依赖 package 时, 使用
default-features = false来关闭它的缺省 feature;
[features]
# 默认启用 default features, 除非显式通过 --no-default-features 或 default-features=false 来关闭。
default = ["ico", "webp"]
# feature 数组元素类型:
# 1. 其它 feature;
# 2. 启用可选依赖:dep:optional_package;
# 3. 启用依赖 package 的 feature:package/feature
bmp = []
png = []
ico = ["bmp", "png"] # 启用 ico feature 时, 启用 bmp 和 png feature
webp = []
Cargo 默认为可选的 package 创建一个用 package 命名的 feature,值为 dep:optional_package, 后续启用该 feature 时才会引入该可选依赖:
[dependencies]
gif = { version = "0.11.1", optional = true } # 可选依赖
[features]
# cargo 默认为可选依赖创建一个和 package 同名的 feature, 它的值为 'dep:gif'
#gif = ["dep:gif"]
# mygif 依赖上面隐式创建的 gif feature,从而启用该可选依赖
mygif = ["gif"]
但是,如果定义一个 feature 来依赖可选依赖(格式:dep:pkg),则默认不会为可选依赖创建同名 feature:
[dependencies]
ravif = { version = "0.6.3", optional = true }
rgb = { version = "0.8.25", optional = true }
[features]
# 定义 avif feature 时使用了可选依赖,则 cargo 不再隐式创建名为 ravif 和 rgb 的 feature。
# 启用 avif feature 时也启用这两个可选依赖。
avif = ["dep:ravif", "dep:rgb"]
启用依赖包的 feature #
[dependencies]
# 启用该 package 的 derive feature 和 default features
serde = { version = "1.0.118", features = ["derive"] }
# 关闭该 package 的 default feature, 只启用 zlib feature
flate2 = { version = "1.0.3", default-features = false, features = ["zlib"] }
也可以在 [features] 中启用依赖包的 features:
[dependencies]
# 没有启用该 package 的任何 feature
jpeg-decoder = { version = "0.1.20", default-features = false }
[features]
# 启用 parallel feature 时启用 jpeg-decoder(不需要为可选包)的 rayon feature
parallel = ["jpeg-decoder/rayon"]
上面的语法中,如果 package 是 optional 的则会启用该 package。如果不想启用它, 则需要使用 package-name?/feature-name 语法,这样只有通过其它方式启用这个可选依赖时,才会启用这个 feature:
[dependencies]
serde = { version = "1.0.133", optional = true }
rgb = { version = "0.8.25", optional = true }
[features]
# 如果其它 feature 启用了 rgb 依赖, 这时才启用 rgb 的 serde feature
serde = ["dep:serde", "rgb?/serde"]
cargo 命令行的 features 参数 #
--features FEATURES:- 启用列出的 feature,多个 feature 可以用逗号或空格分隔。如
--features "foo bar"。 - 如果在 workspace 中构建多个 package,可以使用
package-name/feature-name语法为特定 workspace 成员指定 feature。
- 底层传给 rustc 的 –cfg 选项, 如
--cfg 'feature="foo" feature="bar"';
- 启用列出的 feature,多个 feature 可以用逗号或空格分隔。如
--all-features: 激活命令行选择的所有 package 的所有 feature。--no-default-features: 不激活选择的 package 的 default feature。
缺省情况下, cargo build/test/bench/docs 和 clippy 等只会编译 default features (除非传递 –no-default-features)。
profiles #
profile 提供了一种修改编译器参数的方式,如优化级别、调试符号表等。
Cargo 提供了4 种内置的 profiles:dev, release, test, and bench,也可以自定义 profile。
Cargo 只参考 root workspace Cargo.toml 中的 profile 设置, 而忽略 member package Cargo.toml 中的 profile 设置。
package 的 .cargo/config.toml 中的 profile 配置会覆盖 Cargo.toml 中的配置。
profile 参数解释:https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/profiles.html
缺省 profiles:
-
dev:适用于 cargo build 或 cargo install –debug
[profile.dev] opt-level = 0 # 不优化,cfg!(debug_assertions) 为 true debug = true # 带 DWARF 调试符号表 split-debuginfo = '...' # Platform-specific. strip = "none" # 不删除符号表 debug-assertions = true # debug 模式 overflow-checks = true # 检查溢出 lto = false panic = 'unwind' # unwind incremental = true # 增量构建 codegen-units = 256 rpath = false -
release: 适用于加了 –release 选项的命令, 也是 cargo install 的缺省参数:
[profile.release] opt-level = 3 # 高级优化 debug = false # 不含 DWARF 调试符号表 split-debuginfo = '...' # Platform-specific. strip = "none" # 不删除符号表 debug-assertions = false # 不是 debug 模式 overflow-checks = false lto = false panic = 'unwind' incremental = false codegen-units = 16 rpath = false -
test: 用于 cargo test 命令, 复用 dev profile
-
bench: 用于 cargo bench 命令, 复用 release profile
cargo 默认不优化 build script/proc macro 及它们的依赖,即编译 [build-dependencies] 中的 package 时默认不优化。
自定义 profile:
[profile.release-lto]
inherits = "release"
lto = true
后续使用 –profile
cargo build --profile release-lto
Profile 选择:默认根据指定的命令,自动选择的 profile:
- cargo run, cargo build, cargo check, cargo rustc:
devprofile - cargo test:
testprofile - cargo bench:
benchprofile - cargo install:
releaseprofile
可以使用 --profile=NAME 来选择指定的 profile,--release 等效于 --profile=release。
指定的 profile 适用于所有 cargo target: lib/bin/examples/tests/benchs
也可以按照 profile 为指定的 package 设置参数(优先级从高到低):
[profile.dev.package.name]— A named package.[profile.dev.package."*"]— For any non-workspace member.[profile.dev.build-override]— Only for build scripts, proc macros, and their dependencies.[profile.dev]— Settings in Cargo.toml.Default valuesbuilt-in to Cargo.
# 为 foo package 指定使用 -Copt-level=3 参数
# 也可指定 package 版本:[profile.dev.package."foo:2.1.0"]
[profile.dev.package.foo]
opt-level = 3
# 为依赖设置缺省值,* 表示所有依赖 packages(不含当前 workspace member package)
[profile.dev.package."*"]
opt-level = 2
# 为 build scripts 和 proc-macros 及其依赖设置参数
[profile.dev.build-override]
opt-level = 0
codegen-units = 256
debug = false # when possible
[profile.release.build-override]
opt-level = 0
codegen-units = 256
workspace #
workspace 是 package 集合(称为 workspace member package),用于对它们进行统一管理(比如指定依赖版本)。
workspace 级别的 Cargo.toml 支持如下配置参数:
[workspace] — Defines a workspace.
resolver — Sets the dependency resolver to use.
members — Packages to include in the workspace.
exclude — Packages to exclude from the workspace.
default-members — Packages to operate on when a specific package wasn’t selected.
package — Keys for inheriting in packages. package 的 author、name 等信息
dependencies — Keys for inheriting in package dependencies. 依赖
lints — Keys for inheriting in package lints.
metadata — Extra settings for external tools.
[patch] — Override dependencies.
[replace] — Override dependencies (deprecated).
[profile] — Compiler settings and optimizations.
cargo build 时使用 workspace Cargo.toml 文件中的 [patch]/[replace]/[profile.*] , 而忽略 member package 中的对应配置(编译器会警告)。
Root Package : Cargo.toml 中包含 [workspace] 和一个同意别的 [package] 定义的 package。
- 注意:不是 workspace.package,而是和 workspace 同级别定义的 package。workspace.package 用于定义可以被 member package 继承使用的信息。
[workspace]
# root package
[package]
name = "hello_world"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["Alice <[email protected]>", "Bob <[email protected]>"]
Virtual workspace : Cargo.toml 只包含 [workspace] 但不含同级别的 [package],这时必须指定 resolver = "2";
- 一般通过
package.edition来自动推导, 但是 virtual workspace 由于没有 package 定义, 所以需要明确指定。
# [PROJECT_DIR]/Cargo.toml
[workspace]
members = ["hello_world"]
exclude = ["crates/foo", "path/to/other"]
resolver = "2" # Virtual workspace 时,必须指定该配置
# [PROJECT_DIR]/hello_world/Cargo.toml
[package]
name = "hello_world"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2021"
authors = ["Alice <[email protected]>", "Bob <[email protected]>"]
选择 workspace 的 package
cargo --package参数用于选择 workspace 的某个 member package。cargo --workspace选择所有 mermber package,如cargo check --workspace对所有 member package 进行检查。
如果没有指定这两个参数, cargo 根据当前目录来判断应该使用那个(些)package:
- 如果是 package 目录, 则使用对应的 package;
- 如果是 virtual workspace 或 workspace root 目录, 则选择 所有 package ;
对于 virtal workspace,通过配置 [workspace.default-members] 参数,在 virtal workspace 根目录下编译时会选择指定的 packages(而非默认的所有 packages):
[workspace]
members = ["path/to/member1", "path/to/member2", "path/to/member3/*"]
default-members = ["path/to/member2", "path/to/member3/foo"] # 在 virtal workspace 根目录下执行 cargo 命令时默认选择列表中的 package
resolver = "2";
各 member package 共享 workspace root 的 Cargo.lock 和构建缓存目录(target/):
- 共享 Cargo.lock: 确保所有 member package 使用相同的依赖版本。
- 共享缓存目录 target/:加快构建速度;
各 member package 可以有自己的 Cargo.toml 和 .cargo/config.toml 文件:
- Cargo.toml:定义自己的 dependencies 以及继承自 workspace 的配置信息,可以继承的信息包括:package/dependencies/lints
- .cargo/config.toml: package 自己的 cargo 配置;
cargo 会检查 member package 及其所有父目录的 .cargo/config.toml 文件,然后按照优先级将相关内容进行 merge。
- worksapce 级别定义的 .cargo/config.toml 文件优先级最低,可以作为所有 member package 的缺省值。
# Workspace 级别配置
# [PROJECT_DIR]/Cargo.toml
[workspace]
members = ["bar", "crates/*"] # 支持 glob 匹配
# 可以被 member package 继承的 package 信息
[workspace.package]
version = "1.2.3"
authors = ["Nice Folks"]
description = "A short description of my package"
documentation = "https://example.com/bar"
# 可以被 member package 继承的依赖信息(member package 不一定使用)
# 这些依赖,可以在 member package 的 dependencies/build-dependencies/dev-dependencies 中使用。
[workspace.dependencies]
cc = "1.0.73"
rand = "0.8.5"
# 不能声明为 optional
regex = { version = "1.6.0", default-features = false, features = ["std"] }
# 统一定义的 lints 规则
[workspace.lints.rust]
unsafe_code = "forbid"
# 统一定义的 metadata
[workspace.metadata.webcontents]
root = "path/to/webproject"
tool = ["npm", "run", "build"]
# member package 配置
# [PROJECT_DIR]/bar/Cargo.toml
[package]
name = "bar"
# 继承 workspace.package 配置信息
version.workspace = true
authors.workspace = true
description.workspace = true
documentation.workspace = true
[dependencies]
# 继承自 workspace.dependencies 的定义的依赖信息(如版本、features 等),并额外增加的 features
regex = { workspace = true, features = ["unicode"] }
[build-dependencies]
# 继承自 workspace.dependencies 中定义的 cc 依赖信息
cc.workspace = true
[dev-dependencies]
rand.workspace = true
# 继承自 workspace 的 lints
[lints]
workspace = true
.cargo/config.toml 文件 #
https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/config.html
Cargo 的配置方式包括 4 种类型:
- Cargo.toml: 也称 manifest 文件,可以引用 config.toml 中的配置,如 registry;
- config.toml: by package 的 .cargo/config.toml 或用户缺省的 ~/.cargo/config.toml 文件。
- 可以覆盖 Cargo.toml 中的部分配置,如 profile。
- CARGO_XX 环境变量来配置 config.toml 中支持的参数:如
target.x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu.runner对应CARGO_TARGET_X86_64_UNKNOWN_LINUX_GNU_RUNNER; carog --config可以配置 config.toml 中支持的参数:如cargo --config net.git-fetch-with-cli=true fetch,可以多次指定--config,参数会被 merge。
优先级:命令行参数 》环境变量 》配置文件
各种配置中的 binary 或 path 路径:
- 环境变量、命令行参数中:相对于当前工作目录;
- 配置文件中的 binary:如果没有路径分隔符,则在 PATH 搜索。
- 配置文件中的目录:如果不是绝对路径,则相对于 .cargo/ 所在的目录。
[target.x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu]
runner = "foo" # 使用 PATH 搜索 foo
[source.vendored-sources]
directory = "vendor" # 相对于 .cargo 所在的目录,如 /my/project/.cargo/config.toml 对应 /my/project/vendor
命令行指定配置参数:
cargo --config http.proxy="http://example.com"
# 配置参数和值之间可以有空格
cargo --config "net.git-fetch-with-cli = true"
# 对于 TOML 数组,使用 [] 字符串值;
cargo --config 'build.rustdocflags = ["--html-in-header", "header.html"]' …
# 复杂的配置参数
cargo --config "target.'cfg(all(target_arch = \"arm\", target_os = \"none\"))'.runner = 'my-runner'" …
cargo --config profile.dev.package.image.opt-level=3
cargo 在多级目录中查找 .cargo/config.toml 文件:如果当前工作目录是 /projects/foo/bar/baz/,则 cargo 读取 config.toml 的顺序:
- 所以,可以在 worksapce 级别的 .cargo/config.toml 文件中定义缺省配置。
/projects/foo/bar/baz/.cargo/config.toml
/projects/foo/bar/.cargo/config.toml
/projects/foo/.cargo/config.toml
/projects/.cargo/config.toml
/.cargo/config.toml
$CARGO_HOME/config.toml # $CARGO_HOME 默认为 ~/.cargo
对于同一个 key,如果在多个 config.toml 中同时配置,则会 merge 到一起,下级目录的配置覆盖前面的配置。
如果当前工作目录是 workspace root,则 cargo 不会读取 member package 下的 .cargo/config.toml 文件。
.cargo/config.toml 配置参数:
build.target: 默认为host arch,指定要编译生成的 target triple 列表,编译结果保存到target/<triple>/目录下;build.rustflags:传递给 rustc 的编译器参数;- 例如
build.rustflags = ["-C", "link-arg=-fuse-ld=mold"]等效于rustc -C link-arg=-fuse-ld=mold;
- 例如
env: 传递给 build script、rustc、cargo run、cargo build 等 cargo 启动的进程的额外环境变量;target.<triple>.runner:如果指定,在运行 cargo run, cargo test 和 cargo bench 时将生成的 binary 作为 runner 的参数;
对于传递给 rustc 的编译器参数 rustflags,优先级如下(使用第一个):
CARGO_ENCODED_RUSTFLAGS环境变量;RUSTFLAGS环境变量;- 所有匹配
target.<triple>.rustflags和target.<cfg>.rustflags的配置参数会 merge 到一起; build.rustflags配置值;
.cargo/config.toml 配置示例:
# https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/config.html
# path dependency overrides,重载 Cargo.toml 中的 dependencies
# 路径指向包含 Cargo.toml 文件的目录,rustc 会自动解析 package 名称和版本等信息。
paths = ["/path/to/override"]
# cargo 命令别名
[alias]
# cargo b 等效为 cargo build
b = "build"
c = "check"
t = "test"
r = "run"
rr = "run --release"
recursive_example = "rr --example recursions" # alias 支持递归定义
space_example = ["run", "--release", "--", "\"command list\""]
[build]
jobs = 1 # number of parallel jobs, defaults to # of CPUs
rustc = "rustc" # the rust compiler tool
rustc-wrapper = "…" # run this wrapper instead of `rustc`
rustc-workspace-wrapper = "…" # run this wrapper instead of `rustc` for workspace members
rustdoc = "rustdoc" # the doc generator tool
# build for the target triple (ignored by `cargo install`)
target = ["x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu", "i686-unknown-linux-gnu"]
target-dir = "target" # path of where to place all generated artifacts
rustflags = ["…", "…"] # custom flags to pass to all compiler invocations
rustdocflags = ["…", "…"] # custom flags to pass to rustdoc
incremental = true # whether or not to enable incremental compilation
dep-info-basedir = "…" # path for the base directory for targets in depfiles
[target.<triple>] # 特定 target triple 的参数
linker = "…" # linker to use
runner = "…" # wrapper to run executables
rustflags = ["…", "…"] # custom flags for `rustc`
[target.<cfg>] # 匹配 cfg!() 宏的 target 的参数,如 cfg(all(target_arch = "arm", target_os = "none"))
runner = "…" # wrapper to run executables
rustflags = ["…", "…"] # custom flags for `rustc`
[target.<triple>.<links>] # `links` build script override
rustc-link-lib = ["foo"]
rustc-link-search = ["/path/to/foo"]
rustc-flags = ["-L", "/some/path"]
rustc-cfg = ['key="value"']
rustc-env = {key = "value"}
rustc-cdylib-link-arg = ["…"]
metadata_key1 = "value"
metadata_key2 = "value"
[doc]
browser = "chromium" # browser to use with `cargo doc --open`, overrides the `BROWSER` environment variable
[env] # 传给 cargo 命令启动的进程的额外环境变量
# Set ENV_VAR_NAME=value for any process run by Cargo
ENV_VAR_NAME = "value"
# Set even if already present in environment
ENV_VAR_NAME_2 = { value = "value", force = true }
# Value is relative to .cargo directory containing `config.toml`, make absolute
ENV_VAR_NAME_3 = { value = "relative/path", relative = true }
# when to display a notification about a future incompat report
[future-incompat-report]
frequency = 'always'
[cargo-new] # cargo new 参数
vcs = "none" # VCS to use ('git', 'hg', 'pijul', 'fossil', 'none')
[http]
debug = false # HTTP debugging
proxy = "host:port" # HTTP proxy in libcurl format
ssl-version = "tlsv1.3" # TLS version to use
ssl-version.max = "tlsv1.3" # maximum TLS version
ssl-version.min = "tlsv1.1" # minimum TLS version
timeout = 30 # timeout for each HTTP request, in seconds
low-speed-limit = 10 # network timeout threshold (bytes/sec)
cainfo = "cert.pem" # path to Certificate Authority (CA) bundle
check-revoke = true # check for SSL certificate revocation
multiplexing = true # HTTP/2 multiplexing
user-agent = "…" # the user-agent header
[install] # cargo install 参数,默认为 ~/.cargo
root = "/some/path" # `cargo install` destination directory
[net]
retry = 3 # network retries
git-fetch-with-cli = true # use the `git` executable for git operations
offline = true # do not access the network
[net.ssh]
known-hosts = ["..."] # known SSH host keys
[patch.<registry>]
# Same keys as for [patch] in Cargo.toml
[profile.<name>] # Modify profile settings via config.
inherits = "dev" # Inherits settings from [profile.dev].
opt-level = 0 # Optimization level.
debug = true # Include debug info.
split-debuginfo = '...' # Debug info splitting behavior.
strip = "none" # Removes symbols or debuginfo.
debug-assertions = true # Enables debug assertions.
overflow-checks = true # Enables runtime integer overflow checks.
lto = false # Sets link-time optimization.
panic = 'unwind' # The panic strategy.
incremental = true # Incremental compilation.
codegen-units = 16 # Number of code generation units.
rpath = false # Sets the rpath linking option.
[profile.<name>.build-override] # Overrides build-script settings.
# Same keys for a normal profile.
[profile.<name>.package.<name>] # Override profile for a package.
# Same keys for a normal profile (minus `panic`, `lto`, and `rpath`).
[registries.<name>] # registries other than crates.io
index = "…" # URL of the registry index
token = "…" # authentication token for the registry
[registry]
default = "…" # name of the default registry
token = "…" # authentication token for crates.io
[source.<name>] # source definition and replacement
replace-with = "…" # replace this source with the given named source
directory = "…" # path to a directory source
registry = "…" # URL to a registry source
local-registry = "…" # path to a local registry source
git = "…" # URL of a git repository source
branch = "…" # branch name for the git repository
tag = "…" # tag name for the git repository
rev = "…" # revision for the git repository
[term]
quiet = false # whether cargo output is quiet
verbose = false # whether cargo provides verbose output
color = 'auto' # whether cargo colorizes output
hyperlinks = true # whether cargo inserts links into output
progress.when = 'auto' # whether cargo shows progress bar
progress.width = 80 # width of progress bar